- Login
- Sign Up
body::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 7px;
}
body::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
border-radius: 10px;
background: #f0f0f0;
}
body::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
border-radius: 50px;
background: #dfdbdb
}
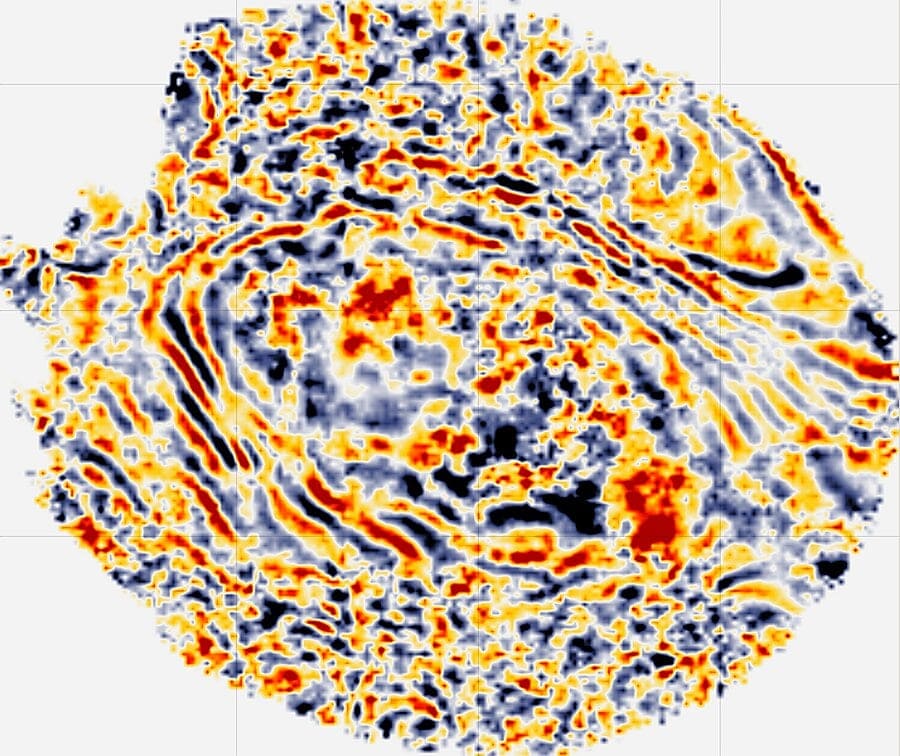
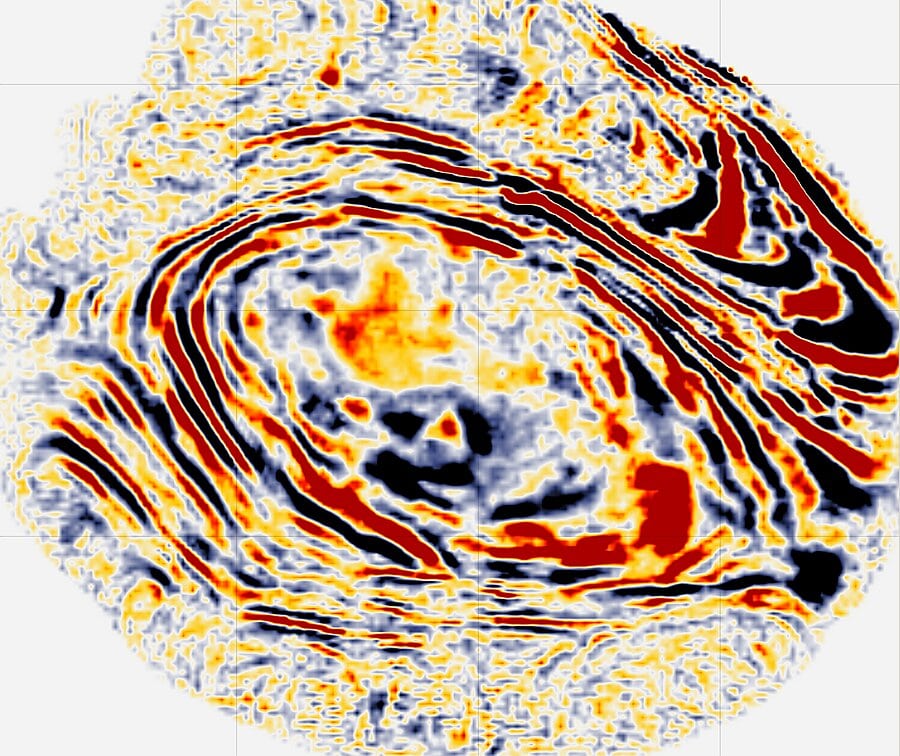
United states – California – Land data – PSTM

Plan g-Viewer
Plan G-Space
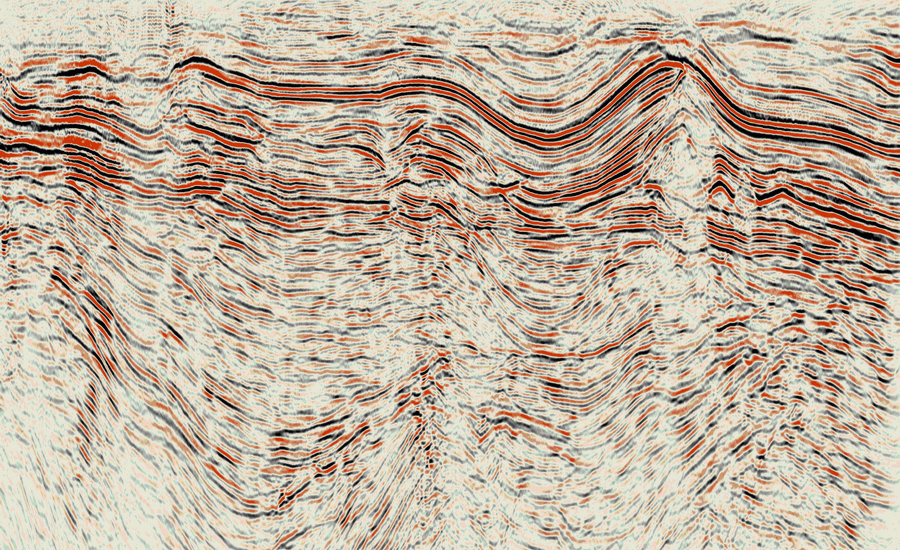

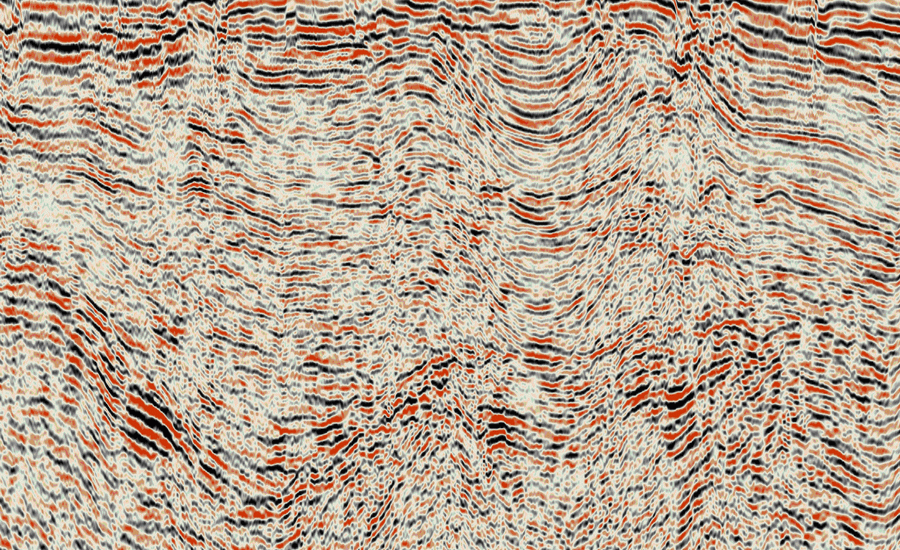
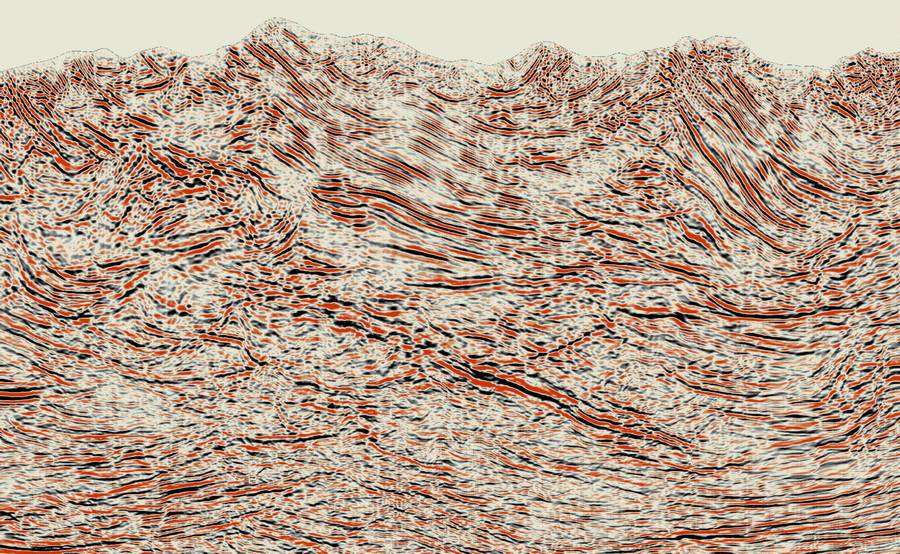

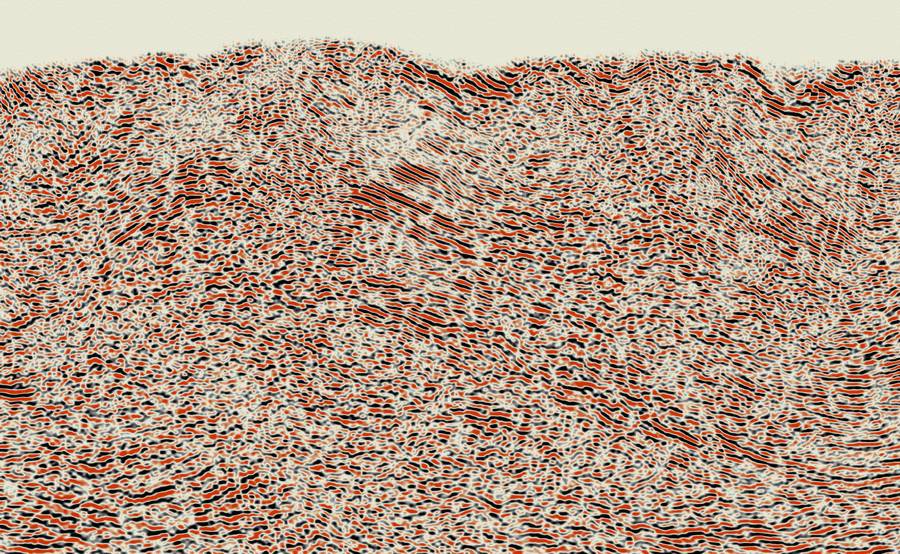
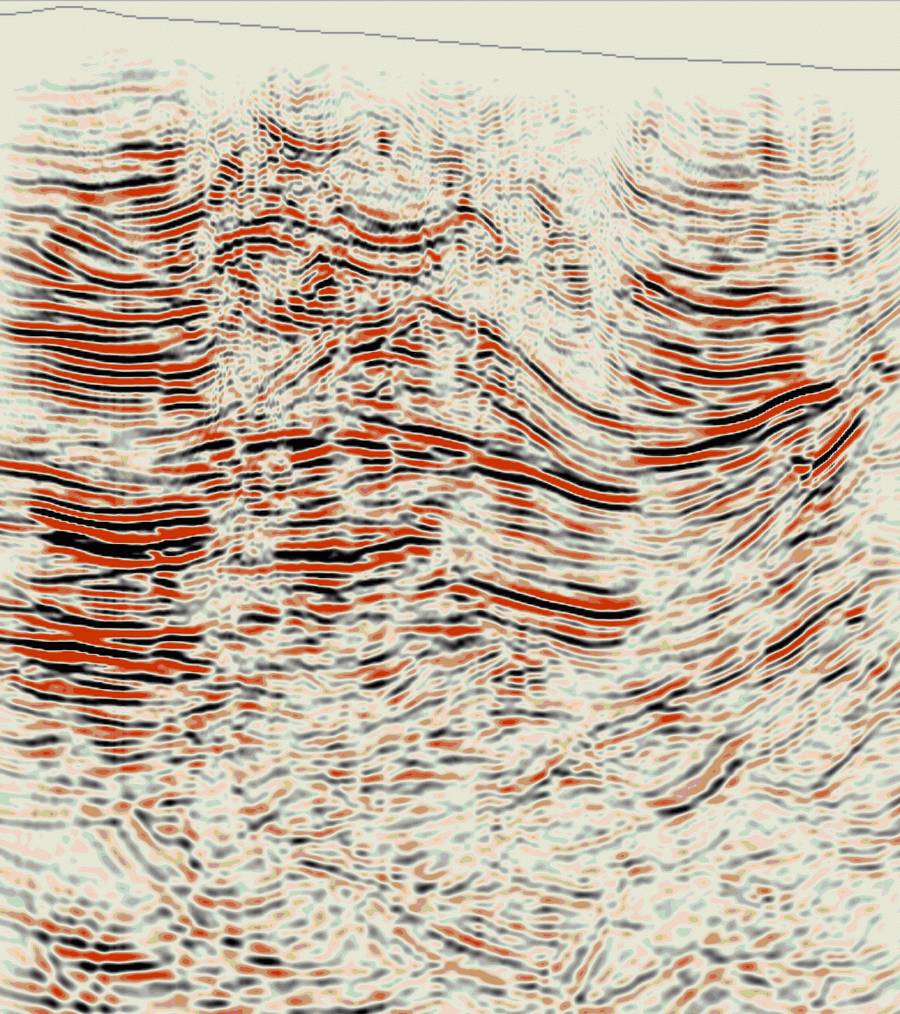

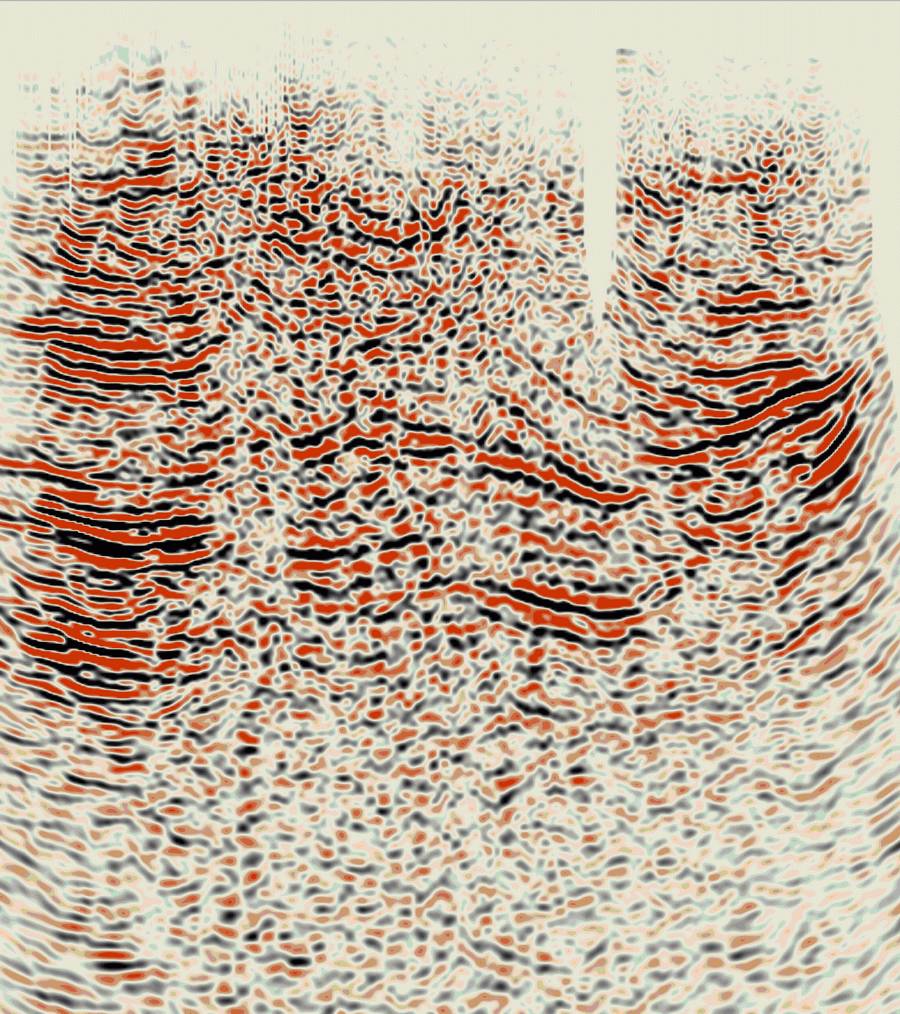




Papua New Guinea



United states – California – Land data – PSTM
[bafg id=”13517″]
Thank you for your message.
[mc4wp_form id=”2437″]
